Russian revolution timeline 1905 to 1924 – The Russian Revolution of 1905-1924 was a pivotal event in world history, marking the overthrow of the Tsarist regime and the establishment of the Soviet Union. This comprehensive timeline delves into the key events, causes, and consequences of this transformative period, providing a nuanced understanding of its profound impact on Russia and beyond.
The early 20th century in Russia was marked by widespread political, economic, and social unrest, which culminated in the 1905 Revolution. The Russo-Japanese War and the Bloody Sunday massacre were pivotal moments that ignited revolutionary sentiments among the masses.
Prelude to Revolution (1905-1914)
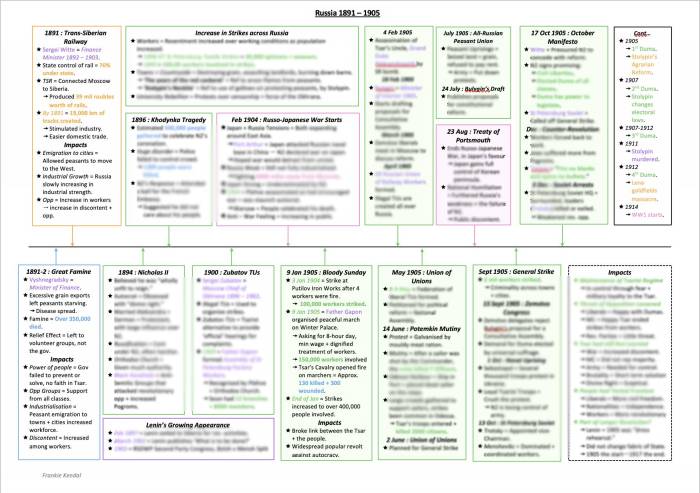
Prior to 1905, Russia faced severe political, economic, and social challenges. The autocratic rule of the Tsarist regime stifled political freedom and hindered economic development. Industrialization led to widespread poverty and labor unrest, while peasants suffered from land shortages and oppressive serfdom.
The Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905) exposed the weakness of the Russian military and government. The defeat humiliated Russia and sparked widespread discontent among the population.
The intelligentsia played a pivotal role in shaping revolutionary sentiment. They criticized the Tsarist regime and advocated for social and political reforms. Revolutionary movements, such as the Social Democrats and the Socialist Revolutionaries, gained traction among the working class and peasantry.
1905 Revolution
The 1905 Revolution began with a peaceful protest in St. Petersburg on Bloody Sunday (January 22, 1905), which ended in a brutal massacre by government troops. The massacre sparked widespread outrage and led to the formation of the St. Petersburg Soviet, a council of workers’ representatives.
The Soviet demanded political reforms, including the establishment of a constitutional monarchy and a representative assembly (Duma). The Tsar responded with limited concessions, but the revolution continued to spread throughout the country, forcing the government to negotiate.
Interregnum (1906-1914)
After the 1905 Revolution, the Tsar introduced political and economic reforms. The Duma was established, but its powers were limited. Political parties emerged, but the Tsarist regime remained authoritarian.
The Balkan Wars (1912-1913) strained Russian foreign policy, as the government sought to expand its influence in the region.
Outbreak of World War I (1914-1917), Russian revolution timeline 1905 to 1924
Russia’s involvement in World War I had a profound impact on the country. The war placed immense strain on the economy and society, leading to food shortages and widespread suffering.
Military failures and heavy casualties eroded public support for the Tsarist regime. The influence of Grigori Rasputin, a self-proclaimed holy man who gained significant influence over the Tsarina, further undermined the government’s legitimacy.
Detailed FAQs: Russian Revolution Timeline 1905 To 1924
What were the main causes of the Russian Revolution?
The Russian Revolution was caused by a complex interplay of factors, including political oppression, economic inequality, and social unrest.
Who were the key leaders of the Russian Revolution?
Vladimir Lenin, Leon Trotsky, and Joseph Stalin were among the most prominent leaders of the Russian Revolution.
What was the impact of the Russian Revolution on world history?
The Russian Revolution had a profound impact on world history, inspiring communist movements around the globe and contributing to the Cold War.