The skeletal system haspi answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey into the depths of the skeletal system with our HASPI answer key. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate workings of our body’s framework, providing a profound understanding of its structure, function, and significance.
Delve into the diverse types of bones that compose our skeletal architecture, unraveling their unique roles in movement, support, and protection. Discover the intricate structure of a typical bone, deciphering the interplay between compact and spongy bone components.
Overview of the Skeletal System
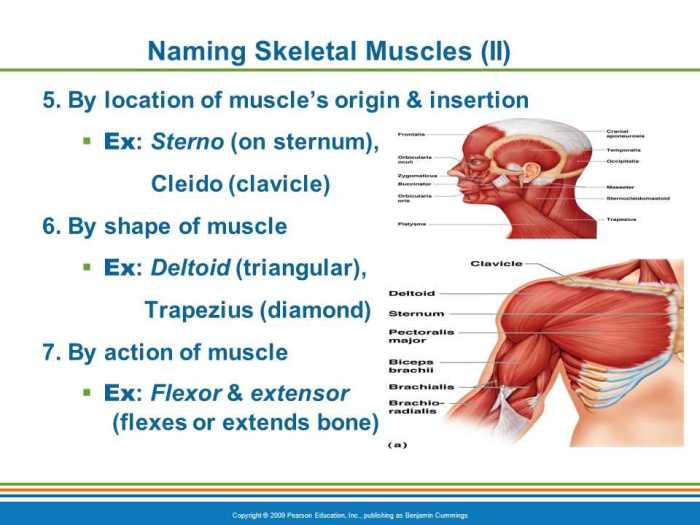
The skeletal system is a complex and essential part of the human body. It consists of bones, cartilage, and ligaments that provide support, movement, and protection for the body’s organs and tissues.
There are different types of bones in the human body, each with its unique structure and function. The main types of bones include long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones.
The skeletal system plays a crucial role in movement, support, and protection. It allows the body to move, provides structural support for the body, and protects the internal organs from injury.
Structure and Function of Bones
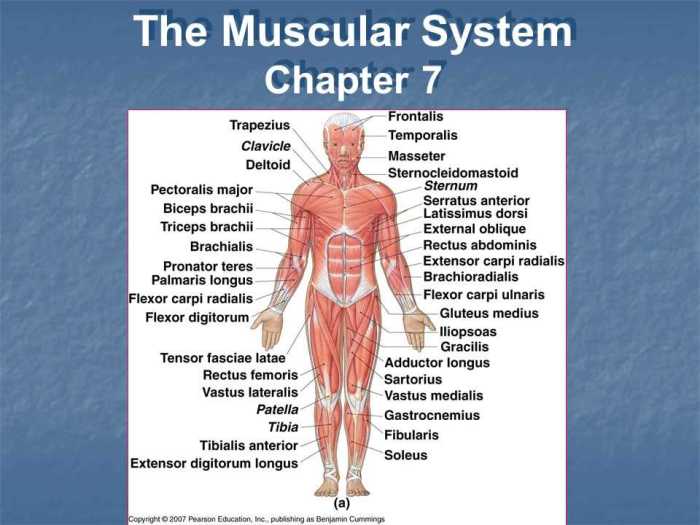
Bones are composed of a hard outer layer called compact bone and a softer inner layer called spongy bone. The compact bone provides strength and rigidity, while the spongy bone is filled with bone marrow and blood vessels.
The periosteum is a thin membrane that covers the outer surface of bones. It contains blood vessels that nourish the bone and cells that repair damaged bone tissue.
The endosteum is a thin membrane that lines the inner surface of bones. It contains cells that line the bone marrow cavity and regulate bone remodeling.
Bone formation and remodeling is a continuous process that occurs throughout life. New bone tissue is constantly being formed to replace old bone tissue.
Major Bones of the Body
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the skull, spine, and rib cage. The skull protects the brain and sense organs. The spine supports the body and protects the spinal cord. The rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
Appendicular Skeleton, The skeletal system haspi answer key
The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the upper limbs (arms and hands) and lower limbs (legs and feet). The upper limbs allow for a wide range of movements, including reaching, grasping, and manipulating objects. The lower limbs provide support for the body and allow for walking, running, and jumping.
Joints and Movement: The Skeletal System Haspi Answer Key

Joints are the points of contact between two or more bones. There are different types of joints in the body, each with its unique structure and function.
Ligaments are tough bands of connective tissue that connect bones together. Tendons are tough bands of connective tissue that connect muscles to bones.
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that covers the ends of bones and provides a smooth surface for movement.
Joint movement is controlled by muscles. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone that it is attached to, causing the joint to move.
Common Bone and Joint Disorders

Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle. It is most common in older adults and can lead to fractures.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation of the joints. It can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling of the joints.
Fractures
Fractures are breaks in the bone. They can be caused by trauma, such as a fall or a car accident.
Q&A
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system provides structural support, facilitates movement, protects vital organs, produces blood cells, and stores minerals.
How many bones are there in the human body?
The average adult human body contains 206 bones.
What is the strongest bone in the body?
The femur, or thigh bone, is the strongest bone in the human body.
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone density, making bones more fragile and susceptible to fractures.
What is the role of cartilage in the skeletal system?
Cartilage provides cushioning and support at the ends of bones within joints, reducing friction and facilitating smooth movement.