In the lexical decision task participants are asked to – In the lexical decision task, participants are asked to identify words quickly and accurately, providing insights into the cognitive processes involved in language processing and word recognition. This task has been widely used in research and clinical settings to study various aspects of language and cognition.
The lexical decision task involves presenting participants with a series of stimuli, which can be either words or non-words, and asking them to indicate whether each stimulus is a word or not. Response times and accuracy are measured, and the results are analyzed to understand the factors that influence lexical access and word recognition.
Lexical Decision Task: Definition and Overview: In The Lexical Decision Task Participants Are Asked To

The lexical decision task is a widely used experimental paradigm in cognitive psychology that measures the speed and accuracy with which participants identify words and non-words.
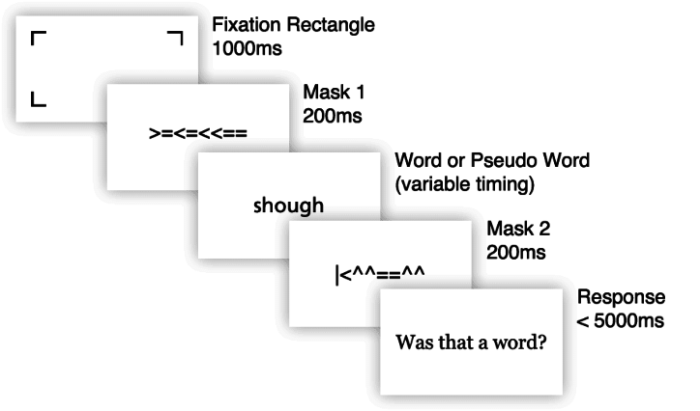
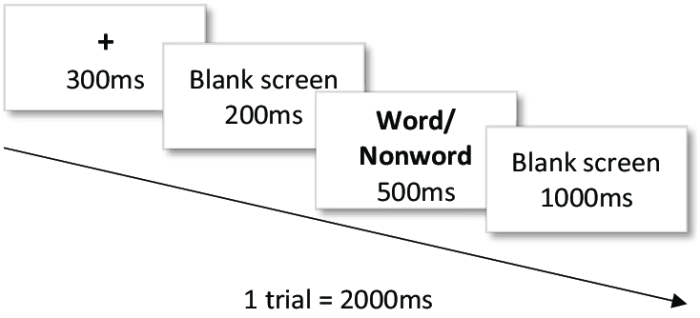
In a typical lexical decision task, participants are presented with a series of letter strings and asked to indicate whether each string is a word or a non-word by pressing one of two designated keys. The letter strings can be presented either visually or auditorily.
Stimuli Used in Lexical Decision Tasks
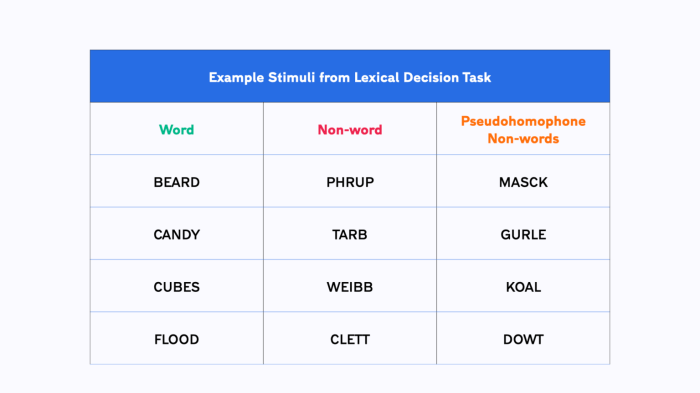
The stimuli used in lexical decision tasks can vary in length, frequency, and orthographic and phonological properties. Common types of stimuli include:
- Real words (e.g., “dog”, “table”, “love”)
- Non-words (e.g., “dorg”, “tafle”, “luve”)
- Pseudowords (e.g., “crimp”, “blert”, “smog”)
Participants’ Instructions
Participants in a lexical decision task are typically given simple instructions, such as:
- Press the “Y” key if the letter string is a word.
- Press the “N” key if the letter string is a non-word.
Participants are usually instructed to respond as quickly and accurately as possible.
Response Times and Accuracy: Measurement and Analysis
Response times and accuracy are two key measures in the lexical decision task.
Response timesare measured in milliseconds (ms) and reflect the time it takes a participant to make a decision about whether a letter string is a word or a non-word.
Accuracyis measured as the percentage of correct responses. Accuracy is typically high in lexical decision tasks, with participants correctly identifying words and non-words at rates of 90% or higher.
Both response times and accuracy can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the length, frequency, and orthographic and phonological properties of the letter strings.
Experimental Design: Variations and Considerations, In the lexical decision task participants are asked to
Lexical decision tasks can be designed in a variety of ways to investigate different aspects of lexical access and word recognition.
One common variation is to manipulate the type of stimulipresented to participants. For example, researchers may compare response times and accuracy for real words, non-words, and pseudowords.
Another common variation is to manipulate the presentation timeof the letter strings. By varying the presentation time, researchers can investigate the time course of lexical access and word recognition.
Cognitive Processes: Lexical Access and Word Recognition
The lexical decision task provides insights into the cognitive processes involved in lexical access and word recognition.
Lexical accessrefers to the process of retrieving a word’s representation from the mental lexicon. Word recognitionrefers to the process of identifying a word once it has been accessed.
The lexical decision task can be used to investigate the time course of lexical access and word recognition, as well as the factors that influence these processes.
Applications and Extensions: Research and Clinical Settings
The lexical decision task has been used in a wide range of research and clinical settings.
In research, the task has been used to investigate various aspects of language processing and cognitive function, such as:
- The time course of lexical access and word recognition
- The effects of word frequency and orthographic and phonological properties on lexical access
- The role of the mental lexicon in language comprehension and production
In clinical settings, the task has been used to assess language impairments in patients with neurological disorders, such as aphasia and dementia.
FAQs
What is the purpose of the lexical decision task?
The lexical decision task is used to study the cognitive processes involved in language processing, particularly lexical access and word recognition.
How is the lexical decision task conducted?
Participants are presented with a series of stimuli (words or non-words) and asked to indicate whether each stimulus is a word or not. Response times and accuracy are measured.
What factors can influence performance on the lexical decision task?
Factors that can influence performance include word frequency, length, and familiarity, as well as individual differences in cognitive abilities.