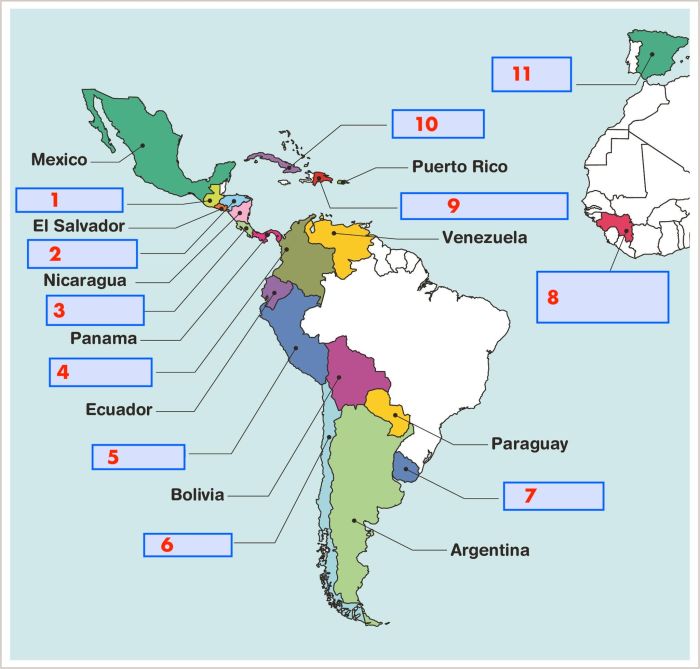
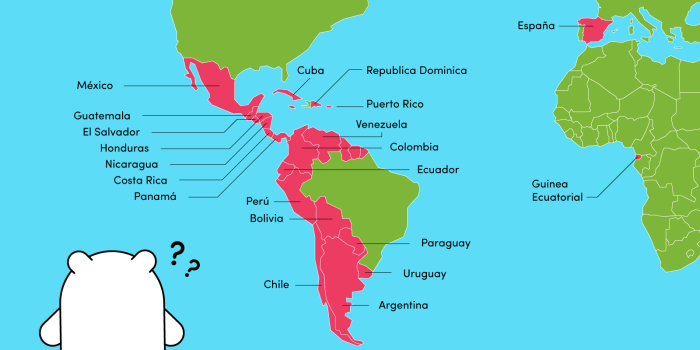
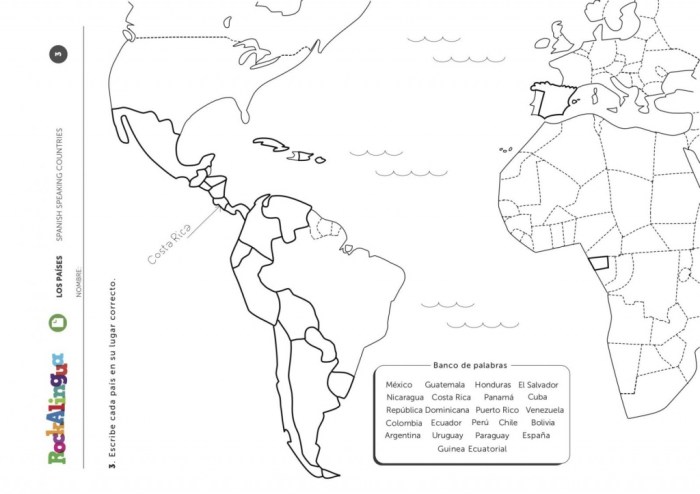
Answer map labeling spanish speaking countries – Answer map labeling plays a crucial role in accurately identifying and representing Spanish-speaking countries on maps. This article delves into the significance, methods, and best practices for labeling Spanish-speaking countries, ensuring clear and effective communication.
Understanding the nuances of labeling Spanish-speaking countries enhances the accessibility and accuracy of maps, fostering a better understanding of global linguistic and cultural diversity.
Introduction: Answer Map Labeling Spanish Speaking Countries
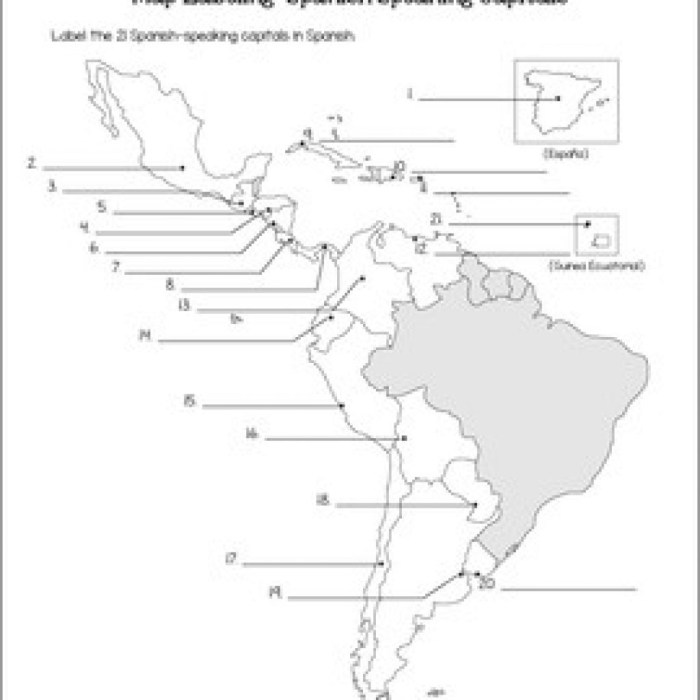
Answer map labeling involves labeling countries on a map with the correct answers to specific questions or topics. It is a crucial skill in geography and education, particularly when dealing with Spanish-speaking countries, due to their global presence and cultural significance.
Methods for Labeling Spanish-Speaking Countries
There are various methods for labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Country Names | Labeling countries with their official names in Spanish | – Accurate and universally recognized
|
– Can be lengthy for larger countries
|
| Country Codes | Labeling countries with their two-letter ISO 3166 codes | – Concise and easy to read
|
– Not as informative as country names
|
| Flags | Labeling countries with their national flags | – Visually appealing and easy to recognize
|
– Can be difficult to distinguish between similar flags
|
| Colors | Labeling countries with different colors | – Can be used to highlight specific regions or groups
|
– May be confusing if colors are not used consistently
|
Examples of Answer Map Labeling, Answer map labeling spanish speaking countries
Effective answer maps that label Spanish-speaking countries include:
- Political mapsthat show the boundaries and names of Spanish-speaking countries
- Language mapsthat highlight the distribution of Spanish-speaking populations
- Historical mapsthat depict the expansion and contraction of Spanish-speaking territories
Considerations for Labeling Spanish-Speaking Countries
When labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps, it is important to consider:
- Cultural sensitivity: Using the correct names and spellings of countries and their cities
- Linguistic diversity: Recognizing the different dialects and variations of Spanish spoken in different countries
- Geographic factors: Ensuring that labels are placed clearly and do not obscure other important features on the map
Best Practices for Answer Map Labeling
To create effective answer maps that label Spanish-speaking countries, follow these best practices:
- Use clear and concise labels: Avoid using long or complex names that may be difficult to read
- Choose appropriate font size and color: Make sure the labels are legible and stand out from the map background
- Place labels carefully: Avoid placing labels over important features or in areas that are difficult to see
- Consider using a combination of labeling methods: For example, using country names for large countries and country codes for smaller ones
Question Bank
What is the significance of labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps?
Labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps is essential for accurately representing linguistic diversity and facilitating communication. It enables individuals to easily identify and locate Spanish-speaking countries, fostering a better understanding of global cultural and linguistic landscapes.
What factors should be considered when labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps?
When labeling Spanish-speaking countries on maps, it is important to consider cultural, linguistic, and geographic factors. Cultural considerations include the preferred language usage and variations within Spanish-speaking countries. Linguistic considerations involve the choice of language (Spanish or English) and the use of appropriate terminology.
Geographic considerations include the accurate placement of labels and the use of appropriate scale and font size.